TRUNCATE
The TRUNCATE statement removes all data from the table in a non-transactional way. TRUNCATE can be thought of as semantically the same as DROP TABLE + CREATE TABLE with the previous definition.
Both TRUNCATE TABLE tableName and TRUNCATE tableName are valid syntax.
Synopsis
TruncateTableStmt:
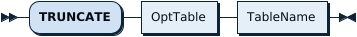
OptTable:

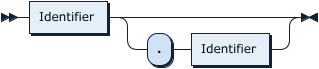
TableName:
Examples
mysql> CREATE TABLE t1 (a INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.11 sec)
mysql> INSERT INTO t1 VALUES (1),(2),(3),(4),(5);
Query OK, 5 rows affected (0.01 sec)
Records: 5 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> SELECT * FROM t1;
+---+
| a |
+---+
| 1 |
| 2 |
| 3 |
| 4 |
| 5 |
+---+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> TRUNCATE t1;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.11 sec)
mysql> SELECT * FROM t1;
Empty set (0.00 sec)
mysql> INSERT INTO t1 VALUES (1),(2),(3),(4),(5);
Query OK, 5 rows affected (0.01 sec)
Records: 5 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> TRUNCATE TABLE t1;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.11 sec)
MySQL compatibility
This statement is understood to be fully compatible with MySQL. Any compatibility differences should be reported via an issue on GitHub.
See also
Was this page helpful?